Fired heaters, commonly known as furnaces or process heaters, are integral components of refineries, petrochemical plants, and other industrial facilities. These equipment are designed to generate the high temperatures necessary for various processes such as distillation, cracking, reforming, and hydrotreating. While fired heaters play a crucial role in the production of fuels and chemicals, their operation poses significant safety risks that must be effectively managed to protect personnel, assets, and the environment.
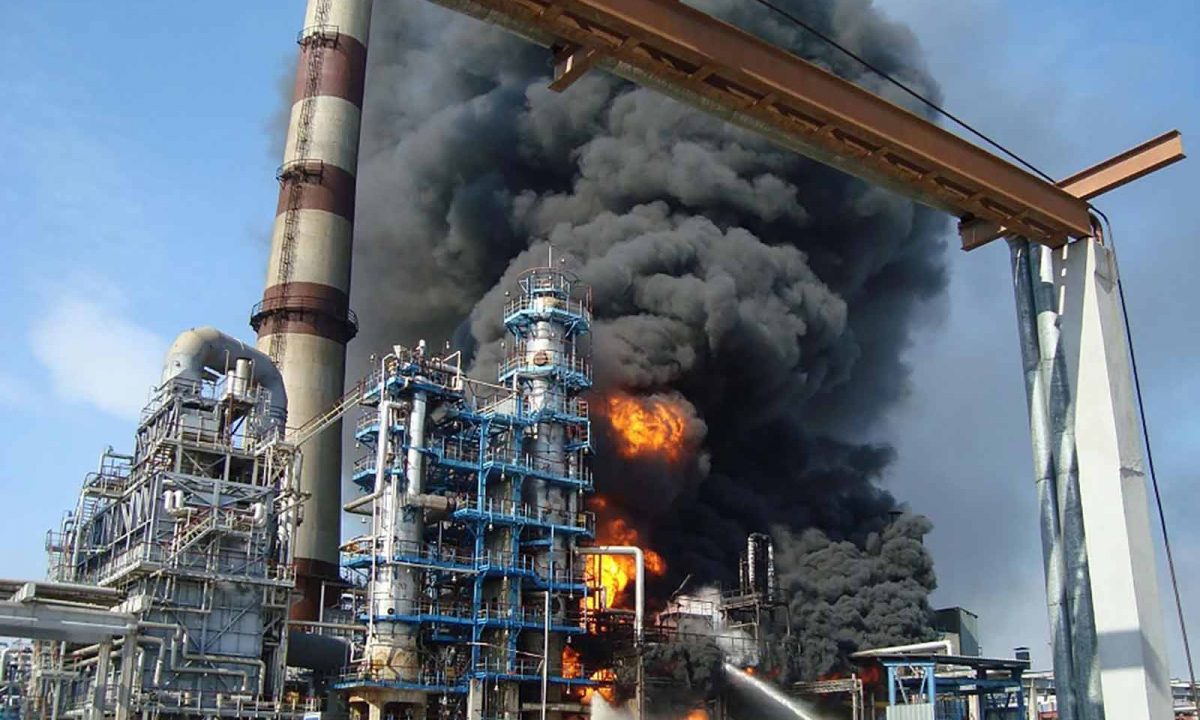

Serious fire incident at Petroleum facility
The safe operation of fired heaters is of utmost importance in refinery operations due to the hazardous nature of the processes involved. These units operate under extreme conditions, including high temperatures, pressure, and the presence of flammable materials, making them susceptible to various safety hazards. Failure to implement proper safety measures can result in catastrophic accidents, fires, explosions, and environmental damage, leading to loss of life, property damage, and financial losses.
Ensuring the safety of fired heaters involves adherence to stringent safety regulations, industry standards, and best practices. One such standard that governs the design, construction, and operation of fired heaters is API 560, published by the American Petroleum Institute (API). API 560 provides comprehensive guidelines for the design, materials, fabrication, inspection, testing, and preparation for shipment of fired heaters for general refinery service.
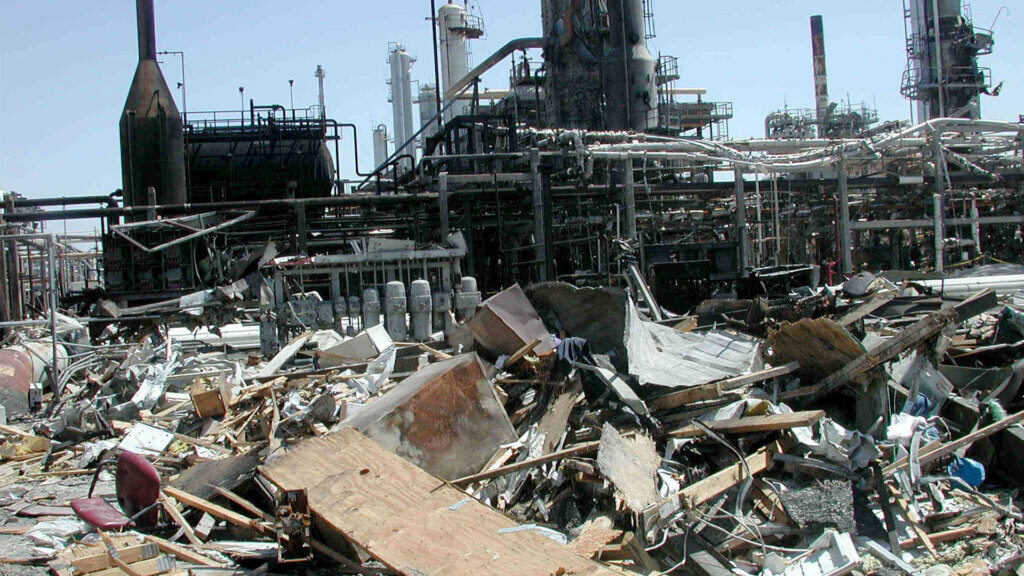

Refinery explosion damage
API 560 sets forth the requirements for fired heaters used in refineries and petrochemical plants, aiming to ensure their safe and reliable operation. The standard covers various aspects of fired heater design and construction, including:
Trend analysis by occupational accident rate published by the Dept. of Statistics Malaysia
Adhering to API 560 standards is essential for ensuring the integrity, reliability, and safety of fired heaters. By following the guidelines outlined in the standard, refineries can minimize the risk of accidents, improve operational efficiency, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
API 560 also emphasizes the importance of proper maintenance, inspection, and testing of fired heaters throughout their lifecycle. Regular inspection and preventive maintenance activities help identify potential safety hazards, such as corrosion, erosion, mechanical wear, and burner degradation, before they escalate into serious issues.
Despite the stringent regulations and standards governing fired heater safety, refineries face several challenges in ensuring the safe operation of these critical equipment:

Fired Heater Maintenance at Refinery
The harsh operating conditions within refineries, including high temperatures, pressure, and the presence of corrosive chemicals, pose significant challenges for fired heater safety. Maintaining proper operating parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates, is essential for preventing equipment failures and ensuring personnel safety.
Regular maintenance and inspection of fired heaters are essential for identifying potential safety hazards and ensuring equipment integrity. However, scheduling maintenance activities can be challenging in a refinery environment where production schedules are often prioritized over maintenance needs. Additionally, accessing and inspecting certain components of fired heaters, such as internal tubes and refractory linings, can be difficult and time-consuming.
Refineries must have robust emergency preparedness plans in place to respond effectively to potential incidents involving fired heaters. This includes conducting regular emergency drills, implementing communication protocols, and ensuring adequate training for personnel. However, maintaining readiness for emergencies requires ongoing investment in training, equipment, and resources, which can be a challenge for some refineries.

To address the challenges associated with fired heater safety, refineries can implement the following best practices:
Proper training and education of personnel involved in fired heater operations are essential for fostering a safety-conscious culture within refineries. Training programs should cover topics such as equipment operation, emergency response procedures, and compliance with safety standards such as API 560. Ongoing training and refresher courses can help reinforce safety protocols and ensure that personnel are prepared to respond effectively to potential hazards.
Implementing a proactive maintenance and inspection program is critical for identifying and addressing potential safety hazards in fired heaters. This includes scheduling routine inspections, conducting non-destructive testing, and monitoring equipment performance. Refineries should also prioritize maintenance activities based on the criticality of equipment and the likelihood of failure, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to address the most pressing safety concerns.
Developing and maintaining comprehensive emergency response plans is essential for minimizing the impact of incidents involving fired heaters. Refineries should establish clear communication channels, emergency response procedures, and evacuation protocols to ensure that personnel can respond quickly and effectively to emergencies. Regular drills and exercises can help test the effectiveness of emergency plans and identify areas for improvement.
Fired heater safety is a critical aspect of refinery operations that requires diligence, adherence to regulations, and continuous improvement. Compliance with API 560 standards, coupled with proper training, maintenance, and emergency preparedness, is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring the safety of personnel and facilities within refineries. By implementing best practices and fostering a safety-conscious culture, refineries can enhance fired heater safety and protect against potential hazards.