Fired heaters are critical components in petroleum refineries, playing a fundamental role in the process of converting crude oil into valuable petroleum products such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. These heaters utilize the combustion of fuel gases or liquids to generate heat, which is then transferred to process fluids circulating through coils or tubes. While fired heaters are essential for refinery operations, they also pose inherent safety risks due to the presence of flammable materials, high temperatures, and complex combustion processes. Therefore, ensuring the safety and reliability of fired heaters is of utmost importance to protect personnel, assets, and the environment.
Safety Standards and Regulations
The design of fired heaters in refineries is governed by a myriad of safety standards and regulations established by organizations such as the American Petroleum Institute (API), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). These standards provide guidelines for the design, construction, installation, and operation of fired heaters to ensure compliance with safety requirements and mitigate potential hazards.
Burner Design
The design of burners plays a crucial role in the safe and efficient operation of fired heaters. Burners must be carefully engineered to achieve optimal combustion performance while minimizing emissions of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO). Additionally, burner designs should incorporate features such as flame scanners, igniters, and flame arrestors to enhance safety and reliability.
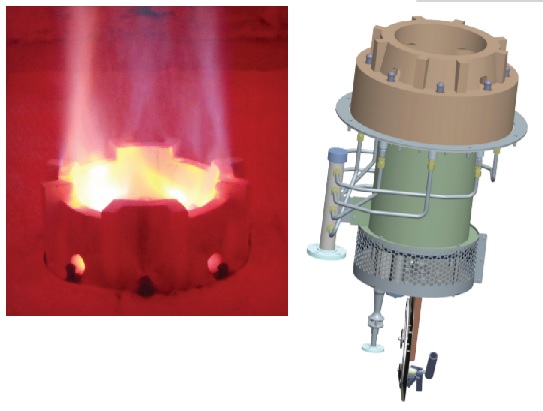
Typical Process Burner in API Fired Heater
Combustion Controls
Advanced combustion control systems are essential for maintaining safe and stable operation of fired heaters. These systems utilize sensors and feedback mechanisms to monitor key parameters such as fuel flow, air-to-fuel ratio, and flame temperature. By continuously adjusting combustion parameters, these controls optimize efficiency, reduce emissions, and prevent potentially hazardous conditions such as flameouts or overheating.
Personnel Training
Proper training of refinery personnel is essential to ensure the safe operation of fired heaters. Operators, maintenance technicians, and other personnel involved in heater operations should receive comprehensive training on equipment operation, safety procedures, emergency response protocols, and regulatory compliance. Ongoing training and refresher courses are necessary to keep personnel updated on the latest safety practices and technologies.

Image title
Operational Procedures
Establishing clear operational procedures is crucial for maintaining safe and efficient operation of fired heaters. Standard operating procedures (SOPs) should outline step-by-step instructions for starting up, shutting down, and operating heaters under normal and abnormal conditions. These procedures should include guidelines for monitoring key parameters, performing routine checks, and responding to alarms or malfunctions.
Routine Inspection and Testing
Regular inspection and testing of fired heaters are essential for identifying potential safety hazards and preventing equipment failures. Inspections should be conducted by qualified personnel according to established schedules and procedures. Key components such as burners, combustion chambers, tubes, and refractory linings should be inspected for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Non-destructive testing techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, and thermal imaging can be used to detect hidden defects or deterioration.

Maintenance Teams
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance programs are designed to proactively address potential issues before they lead to equipment failures or safety incidents. These programs include tasks such as lubrication, cleaning, adjustment, and replacement of worn or degraded components. Preventive maintenance schedules should be based on equipment manufacturer recommendations, industry best practices, and regulatory requirements.
OSHA Regulations
OSHA regulations play a critical role in ensuring the safety of workers in refineries and other industrial facilities. OSHA standards such as 29 CFR 1910.119 (Process Safety Management) and 29 CFR 1910.119 (Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response) establish requirements for process safety, chemical handling, and emergency preparedness in refineries. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for all employers in the United States.

Regulatory Compliance in Oil Refinery
API Standards
The American Petroleum Institute (API) develops industry standards and recommended practices for various aspects of refinery operations, including fired heater safety. API standards such as API STD 560 (Fired Heaters for General Refinery Service) and API RP 556 (Instrumentation and Control Systems for Fired Heaters and Steam Generators) provide guidelines for the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of fired heaters. Adherence to API standards is often considered a best practice in the industry.
NFPA Codes
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) develops codes and standards for fire protection and safety in various industries, including refineries. NFPA standards such as NFPA 86 (Standard for Ovens and Furnaces) and NFPA 87 (Standard for Fluid Heaters) address specific requirements for the safe design, installation, operation, and maintenance of fired heaters and related equipment. Compliance with NFPA codes helps ensure that refineries meet minimum safety standards and reduce the risk of fires and explosions.
Fire Prevention and Suppression
Preventing fires is paramount in refinery operations, but in the event of a fire, prompt and effective suppression is essential to minimize damage and protect personnel and assets. Refineries are equipped with various fire suppression systems such as water-based sprinkler systems, foam systems, and dry chemical systems. Additionally, portable fire extinguishers are strategically located throughout the facility for use in extinguishing small fires or controlling flames until professional responders arrive.
Evacuation Procedures
In the event of a major emergency such as a fire, explosion, or release of hazardous materials, evacuating personnel from the affected area is critical to their safety. Refineries have evacuation procedures in place that outline evacuation routes, assembly points, and communication methods for alerting personnel of the emergency. Emergency evacuation drills are conducted regularly to ensure that personnel are familiar with evacuation procedures and can evacuate safely and efficiently in an emergency.
In conclusion, fired heater safety is a critical aspect of refinery operations that requires careful attention to design, operation, maintenance, and regulatory compliance. By implementing robust safety measures, adhering to industry standards and regulations, and maintaining effective emergency response procedures, refineries can mitigate risks and ensure the safe and reliable operation of fired heaters. Protecting personnel, assets, and the environment from the hazards associated with fired heaters is essential to the long-term success and sustainability of the refinery industry. By prioritizing safety, refineries can prevent accidents, minimize downtime, and maintain the trust and confidence of stakeholders.