Fired heaters, also known as process heaters or furnaces, are critical components in refinery operations, providing the high temperatures necessary for various processes such as distillation, cracking, and reforming. However, the safe design and operation of fired heaters are paramount to ensure the safety of personnel, assets, and the environment within refineries. To achieve this, the American Petroleum Institute (API) has developed standards such as API 530, which provides comprehensive guidelines for the design, inspection, maintenance, and safe operation of fired heaters.

API 530, titled "Calculation of Heater Tube Thickness in Petroleum Refineries," is a standard published by the API that outlines the procedures for calculating the required thickness of tubes used in fired heaters and boilers. The standard covers various aspects of fired heater design, including:
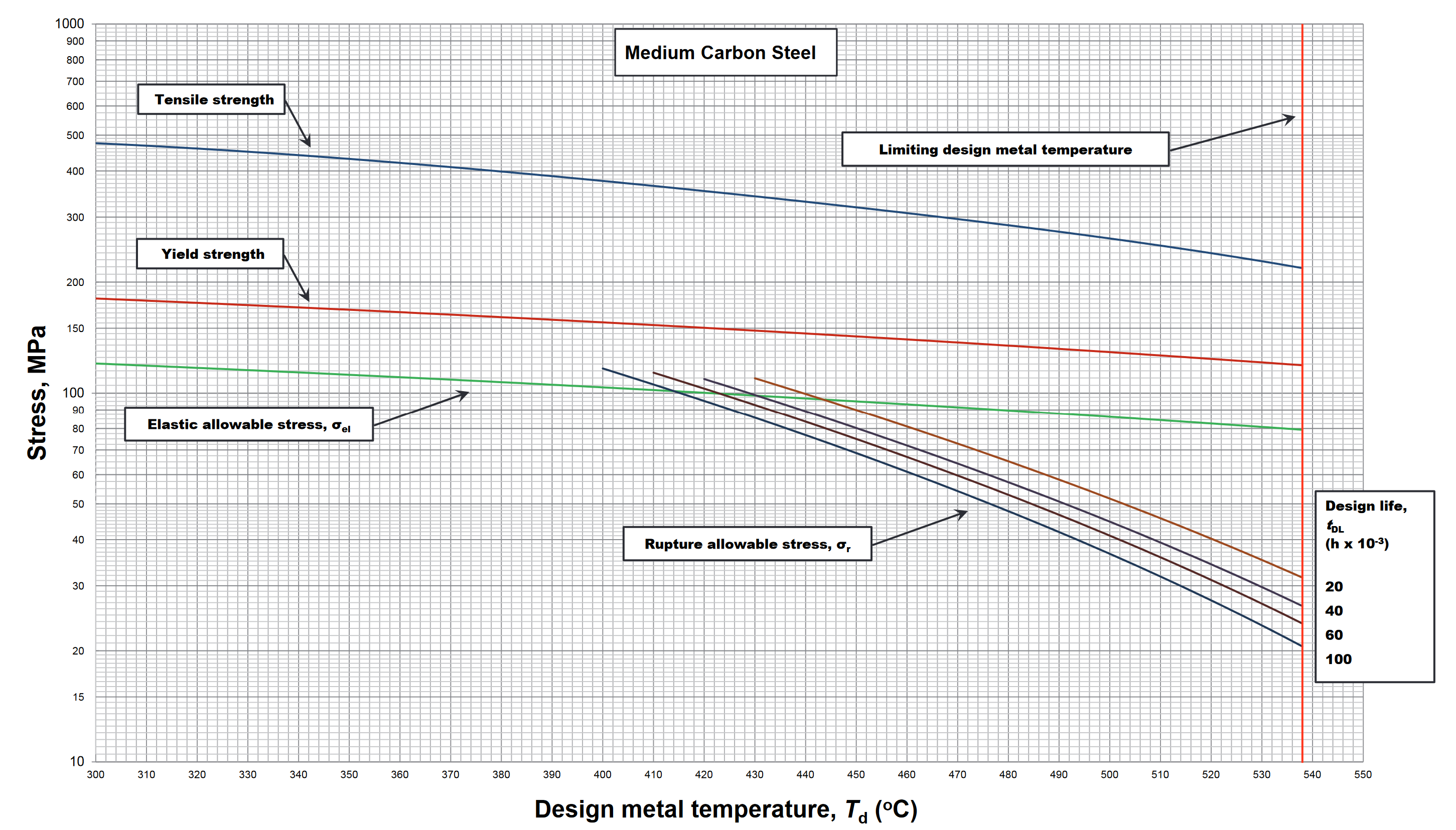
Image title
API 530 is intended to ensure the safe and reliable operation of fired heaters by providing guidelines for designing heaters that can withstand the operating conditions present in refinery processes. Compliance with API 530 helps minimize the risk of equipment failure, accidents, and environmental incidents, thereby enhancing safety and operational efficiency within refineries.
API 530 establishes several key principles and guidelines for the design and operation of fired heaters within refineries:

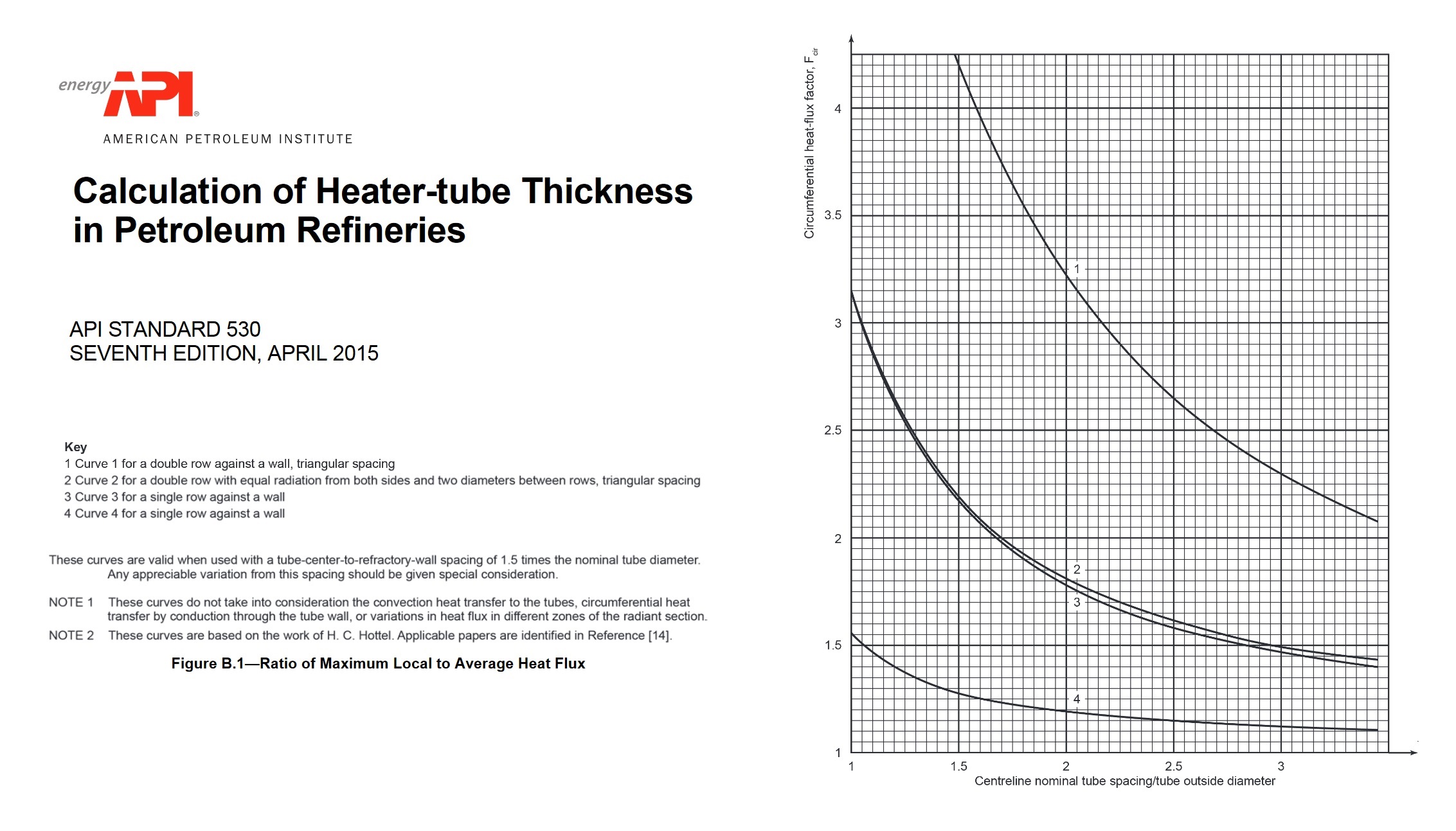
Image title
API 530 specifies the materials that are suitable for use in fired heaters based on their resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and mechanical stresses. Materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steels are commonly used for constructing heater tubes, headers, and other components.
The thermal design of fired heaters involves calculating the heat transfer requirements to achieve the desired process conditions while ensuring that the heater operates safely and efficiently. API 530 provides formulas and procedures for determining heat transfer rates, tube wall temperatures, and other thermal parameters.
The mechanical design of fired heaters focuses on ensuring structural integrity and mechanical stability under operating conditions. This includes determining the required thickness of heater tubes, headers, and other pressure-containing components to withstand internal pressures, external loads, and thermal stresses.
Regular inspection and maintenance of fired heaters are essential for identifying potential safety hazards, such as corrosion, erosion, and mechanical wear, before they escalate into serious issues. API 530 outlines inspection intervals, non-destructive testing methods, and maintenance practices to ensure the continued reliability and safety of fired heaters.

In addition to compliance with API 530, refineries can implement several best practices to enhance the safety and reliability of fired heaters:
Implementing a proactive maintenance program helps identify and address potential issues before they lead to equipment failure or safety incidents. This includes scheduling regular inspections, conducting preventive maintenance activities, and monitoring equipment performance to detect abnormalities.

Fired Heater Maintenance in Refinery
Proper training and education of personnel involved in operating fired heaters are essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation. Training programs should cover topics such as equipment operation, emergency response procedures, and compliance with safety standards such as API 530.
Refineries must have robust emergency preparedness plans in place to respond effectively to potential incidents involving fired heaters. This includes conducting regular emergency drills, establishing communication protocols, and ensuring that personnel are trained to respond to emergencies.
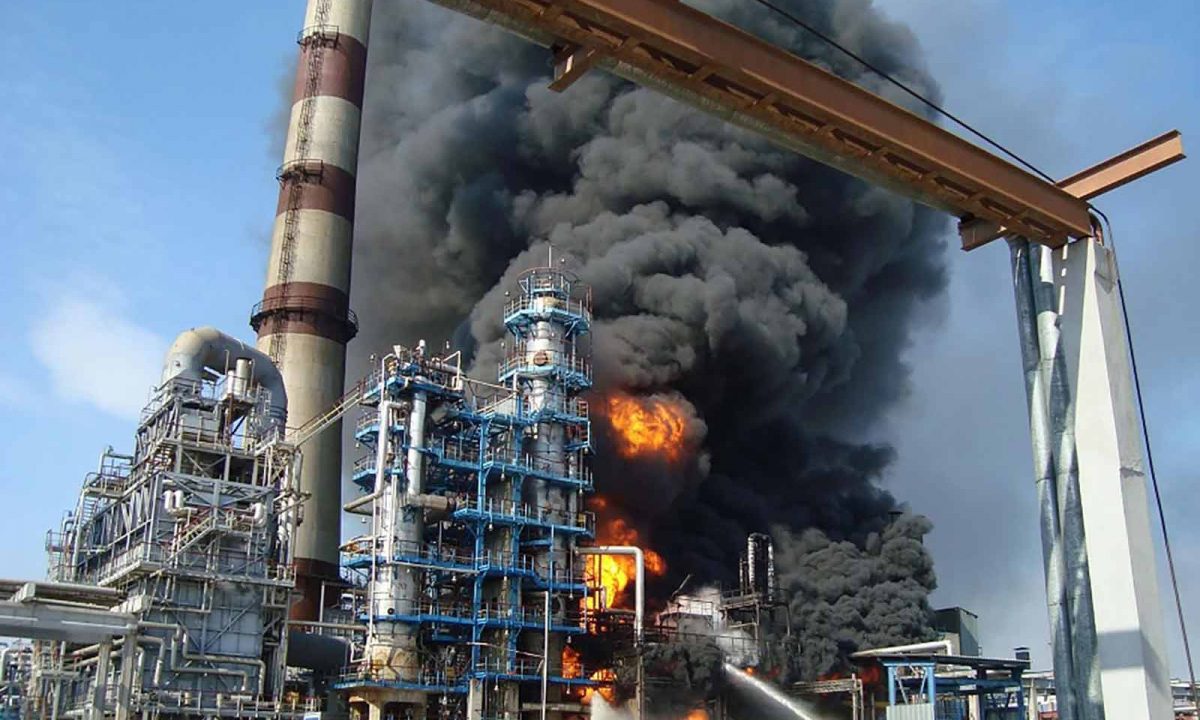

Despite the guidelines provided by API 530 and other industry standards, refineries face several challenges in designing and operating fired heaters:
Fired heaters operate at high temperatures, which can result in thermal stresses, material degradation, and reduced equipment lifespan. To address this challenge, refineries must use high-temperature materials, implement effective insulation systems, and monitor heater performance closely to prevent overheating.
Corrosion and erosion are common issues in fired heaters due to the aggressive nature of refinery processes and the presence of corrosive chemicals. Refineries can mitigate these issues by selecting corrosion-resistant materials, implementing corrosion monitoring programs, and conducting regular inspections to detect corrosion early.
Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, including API 530 and other industry standards, can be challenging for refineries due to the complex nature of fired heater design and operation. Refineries must stay updated on changes to regulations, conduct regular audits to assess compliance, and implement corrective actions as needed to address non-compliance issues.
API 530 plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient design and operation of fired heaters within refineries. By adhering to the guidelines outlined in API 530 and implementing best practices for fired heater safety, refineries can minimize the risk of accidents, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. However, challenges such as high-temperature operations, corrosion, and regulatory compliance require ongoing attention and proactive measures to ensure the continued reliability and safety of fired heaters in refinery operations.