A fired heater detailed engineering project involves a series of crucial milestones that ensure the efficient and safe operation of the heater while meeting industry standards such as API 560. Each activity contributes to the design, safety, and efficiency of the fired heater. Below is a comprehensive overview of the major milestones in such a project.
The first milestone is process design, where the primary process parameters are defined, such as operating temperatures, pressures, and flow rates. This stage involves selecting the appropriate fired heater type and determining the required heat duty to meet process needs. Key considerations include fuel type, excess air ratio, and expected emissions levels.

Pressure part calculation and design focus on ensuring that all components exposed to high pressure meet the necessary safety and regulatory standards. This involves calculating the wall thickness, stress analysis, and material selection for tubes, headers, and drums based on API 530, ASME Section VIII, and other relevant codes.
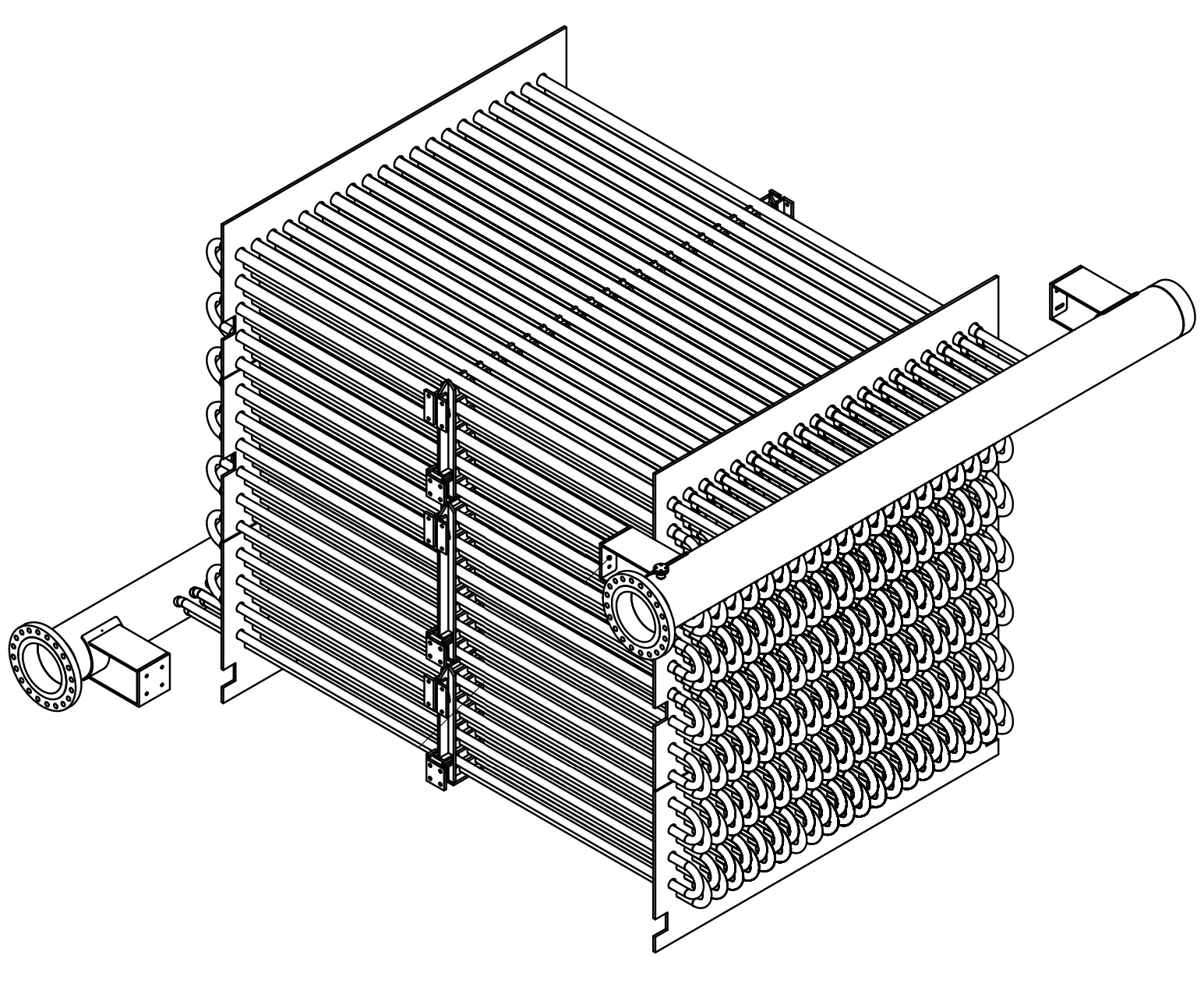
WHRU Convection Coil Bank
Mechanical design ensures that all structural components can withstand the operational conditions, including thermal expansion and vibration. This phase includes detailed design of expansion joints, supports, and the outer casing. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is often used to optimize mechanical integrity.

Image title
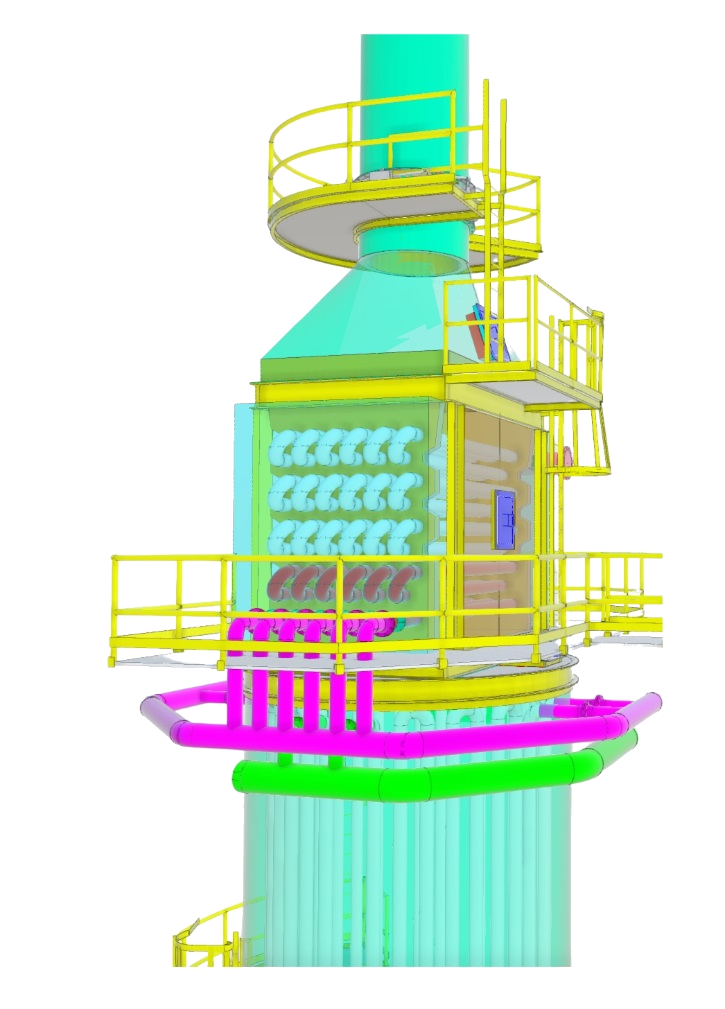
3D modelling is a critical milestone where the fired heater is digitally visualized in a three-dimensional environment. This step allows for better visualization of the entire system, identifying potential clashes and optimizing equipment layout, piping routing, and accessibility for maintenance.
Piping and stress analysis involve designing the piping system connected to the fired heater and ensuring it can withstand thermal expansion and mechanical stress. Pipe stress analysis software like CAESAR II is used to verify that all pipes comply with codes like ASME B31.3, accounting for stress intensification factors (SIFs) and flexibility.
Structural design ensures that the fired heater's supporting structure can withstand both static and dynamic loads, including wind and seismic activity. Structural steel sections are selected based on load calculations, and connections are designed to ensure stability. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) may be used to verify the structural integrity.
Tube supports are crucial for maintaining the alignment and integrity of heater tubes under thermal expansion and operational stresses. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is employed to analyze the tube support designs, ensuring they can withstand the mechanical and thermal loads without deforming or failing.
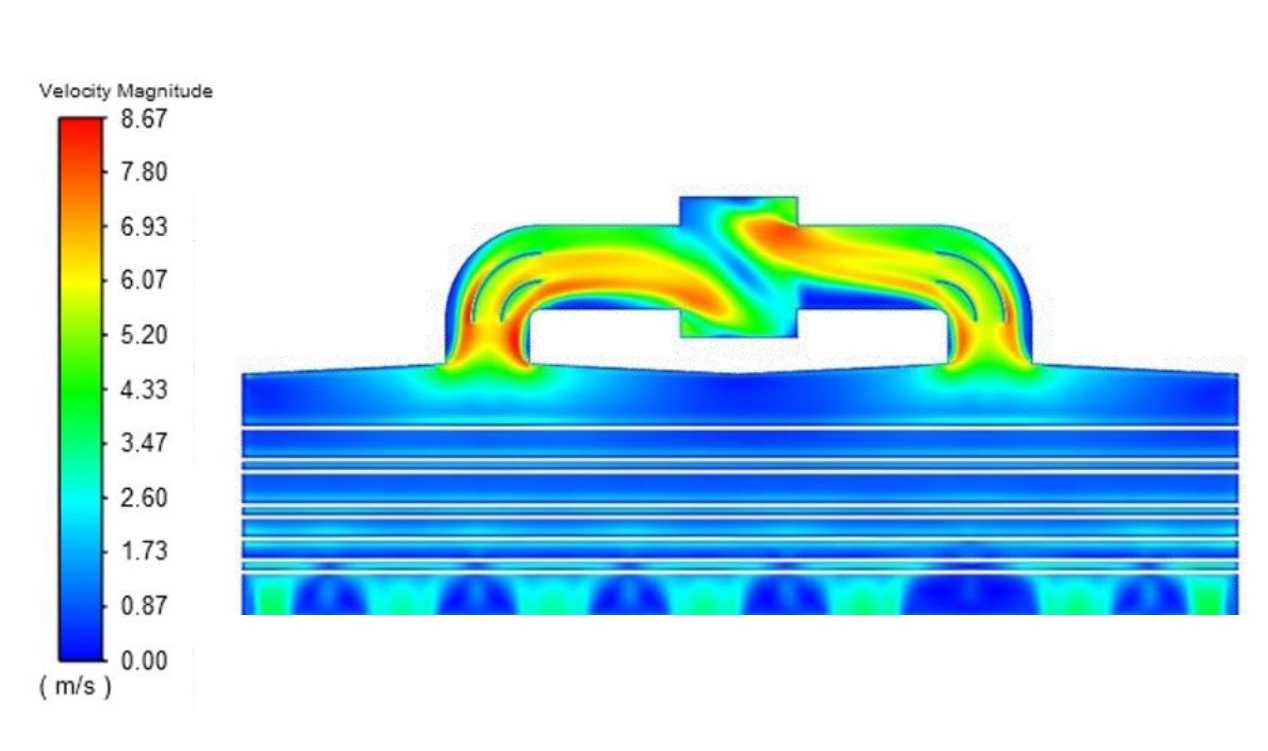
Image title
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modelling is used to simulate the combustion process within the fired heater. This analysis helps optimize burner placement, identify hot spots, and improve heat distribution across the tubes. The goal is to maximize efficiency and minimize emissions while ensuring uniform heat distribution.
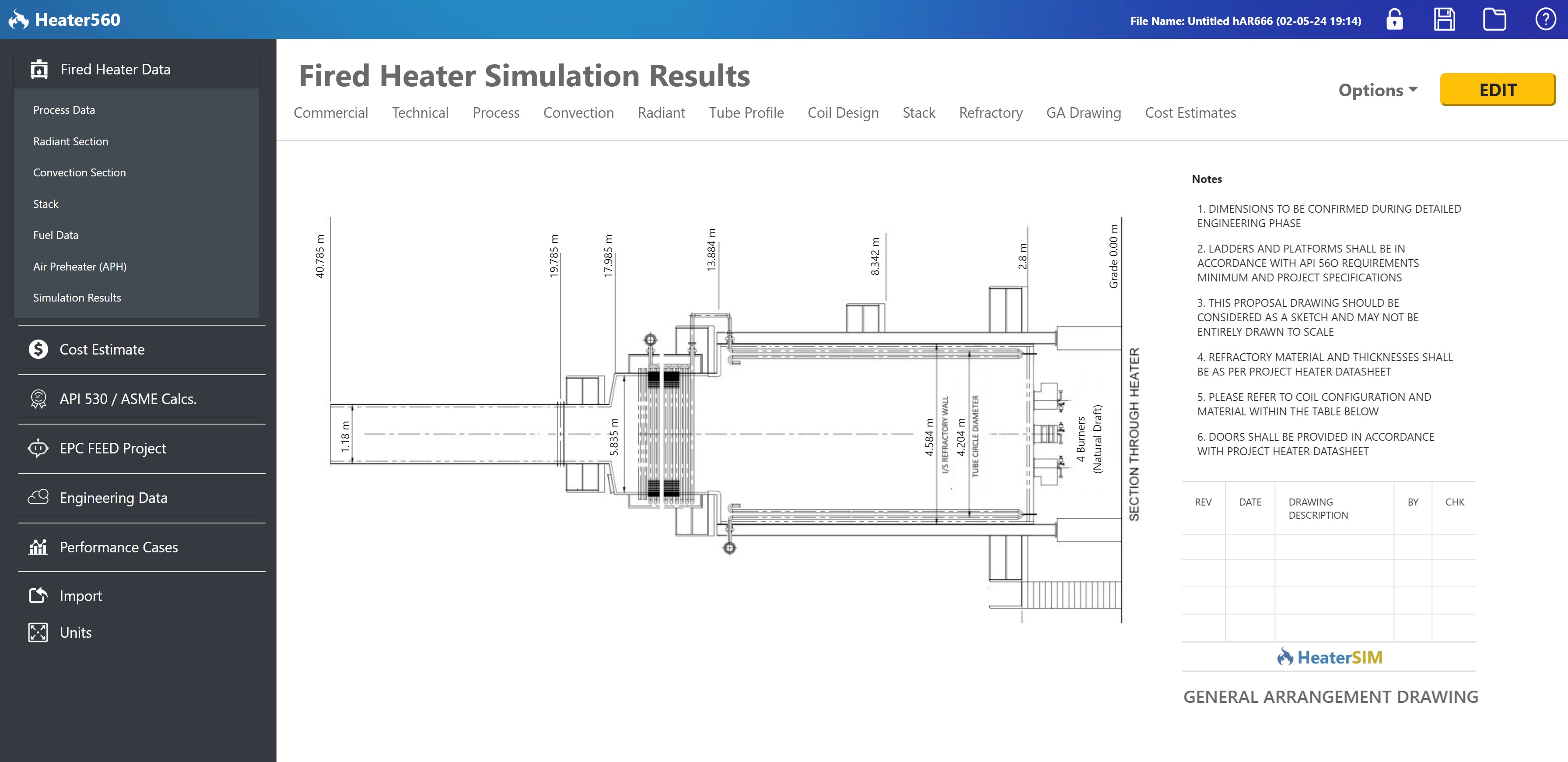
Image title
General Arrangement (GA) drawings provide a comprehensive 2D overview of the fired heater layout. These drawings include plan and elevation views, detailing the position of all major components, piping, and access platforms. GA drawings are crucial for review and approval before fabrication.
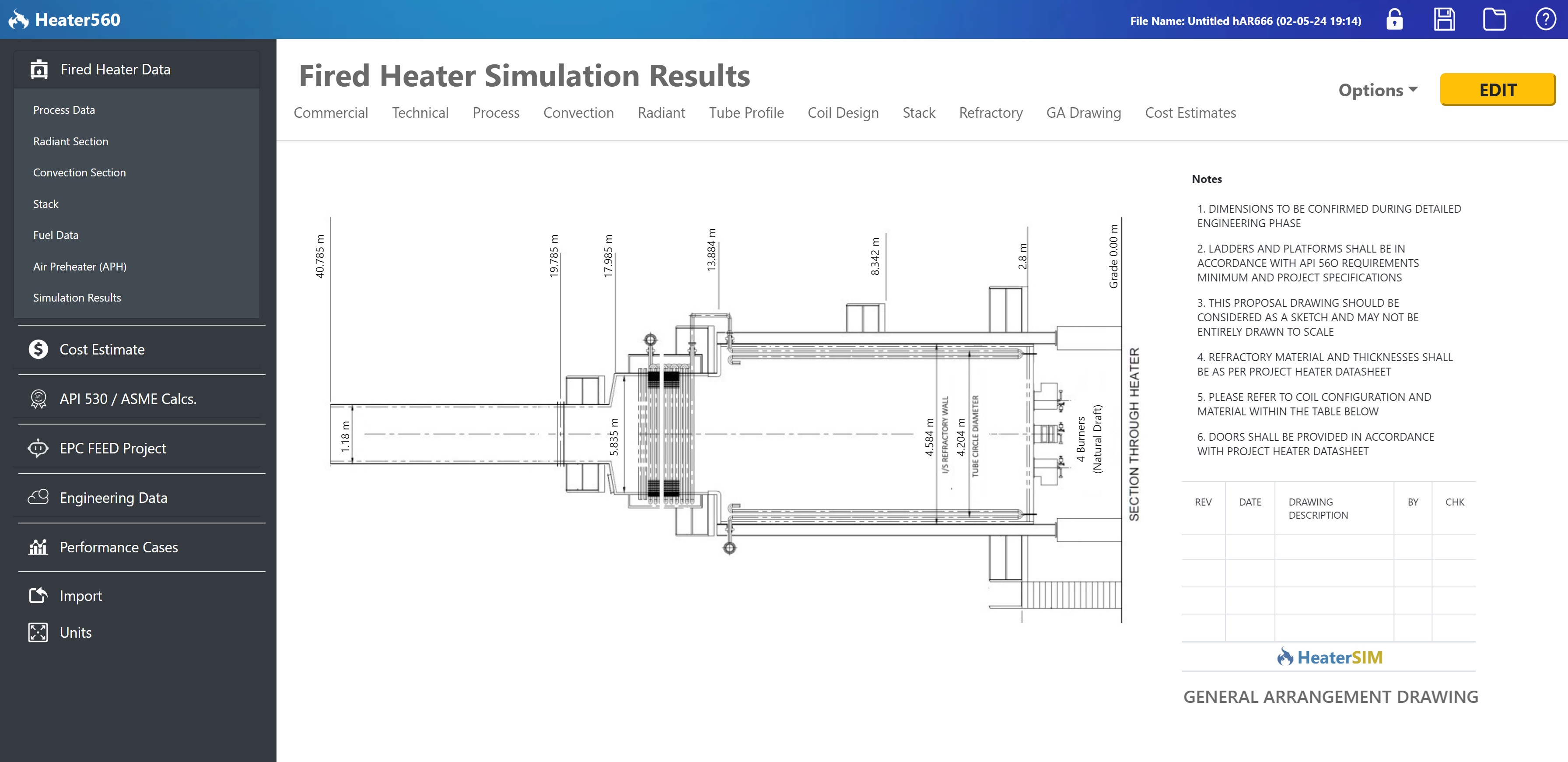
Image title
Fabrication drawings are the final set of detailed drawings that guide the manufacturing process. They include all dimensions, material specifications, welding details, and quality control requirements necessary for the accurate fabrication of fired heater components.
Each milestone in a fired heater detailed engineering project is crucial for delivering a safe, efficient, and compliant heater system. By meticulously following each step, engineers can ensure that the fired heater operates efficiently and reliably, meeting all process requirements and industry standards.